The global climate crisis has heightened the need for accurate reporting and disclosure of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. As organizations worldwide strive to reduce their carbon footprints and achieve sustainability targets, stakeholders require increased confidence in the data and information presented in GHG emissions disclosures. To address this need, the International Standard on Assurance Engagements (ISAE) 3410 was introduced, providing guidance for assurance engagements on GHG statements. In this blog post, we will explore the concepts of limited and reasonable assurance in relation to GHG emissions disclosure and discuss how they contribute to enhanced reporting and corporate accountability. Moreover, we will examine the upcoming Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) GHG disclosure requirements and their implications for assurance engagements.
Types of Assurance
Assurance engagements provide stakeholders with an independent and objective opinion on the reliability and credibility of GHG emissions disclosures. There are two primary types of assurance: limited and reasonable.
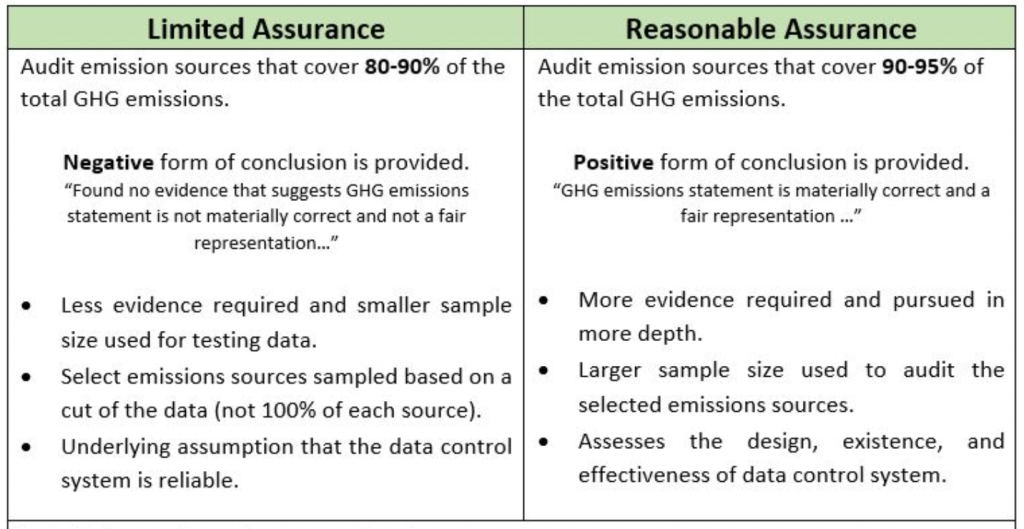
Limited assurance is a lower level of assurance that involves the assurance provider expressing a conclusion about whether they are aware of any material modifications that should be made to the disclosure for it to be in accordance with disclosure requirements. It is equivalent to the assurance provided in an interim review of financial statements. Limited assurance engagements are less rigorous than reasonable assurance but still provide a meaningful level of confidence in the GHG statement. They are more cost-effective, but stakeholders should be aware that they do not offer the same level of confidence as reasonable assurance.
Reasonable assurance, on the other hand, involves the practitioner expressing an opinion about whether the subject matter is in accordance with relevant criteria in all material aspects and free from material misstatement. This level of assurance is equivalent to that provided in an audit. While reasonable assurance is more rigorous and provides higher confidence in the GHG statement, it is also more costly and time-consuming.
ISAE 3410 and its relation to GHG emissions disclosure
ISAE 3410 is designed to provide a framework for assurance engagements on GHG statements, including requirements and guidance for practitioners. The standard outlines key requirements for planning and performing the engagement, obtaining sufficient appropriate evidence, and forming a conclusion based on that evidence.
The role of limited and reasonable assurance in enhancing GHG emissions disclosure
Limited and reasonable assurance play a vital role in improving the quality and credibility of GHG emissions disclosures. Upcoming SEC regulations will require companies to reach limited or reasonable assurance levels when disclosing GHG emission levels. Assurance engagements help increase stakeholder confidence and trust in the reported GHG emissions data. They can also lead to enhanced quality and comparability of GHG statements across organizations. Furthermore, assurance engagements promote corporate accountability and drive sustainability efforts by ensuring accurate and reliable reporting of GHG emissions data.

